AndrewNG-GAN基础
AndrewNG-GAN
Course 1 —— Build Basic GANs
1.1 Introduction
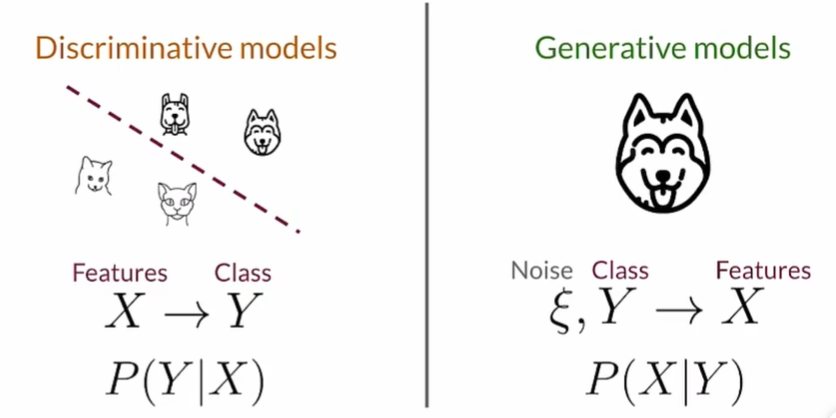
Generative Models:
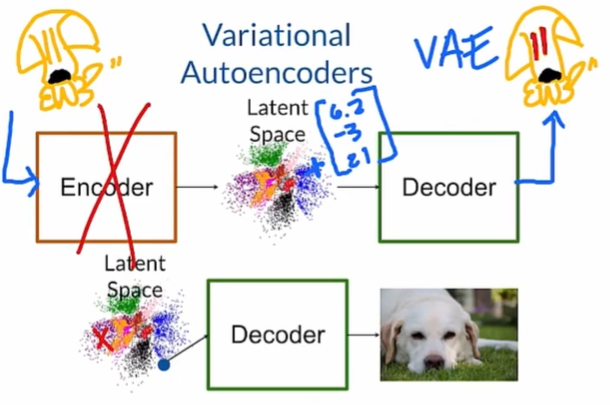
Variational Autoencoders(VAE):
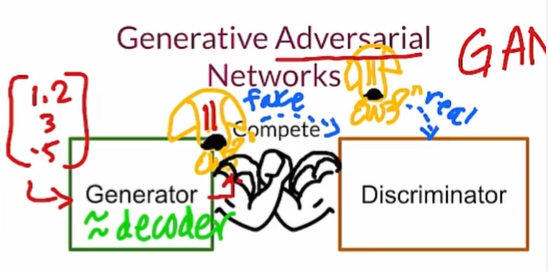
GANS:
GAN in Real Life
- GAN的创始人:Ian Goodfellow
- GAN的应用领域:
- Image Generation, Deep fake
- Text Generation
- Data Augmentaion
- Image Filters
1.2 Basic Components
Discriminator
Use Neural Networks, input: features(image), output: probability
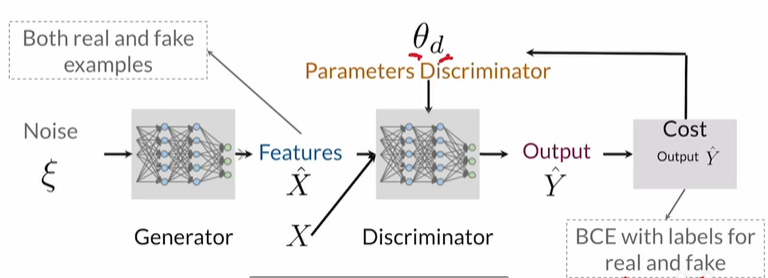
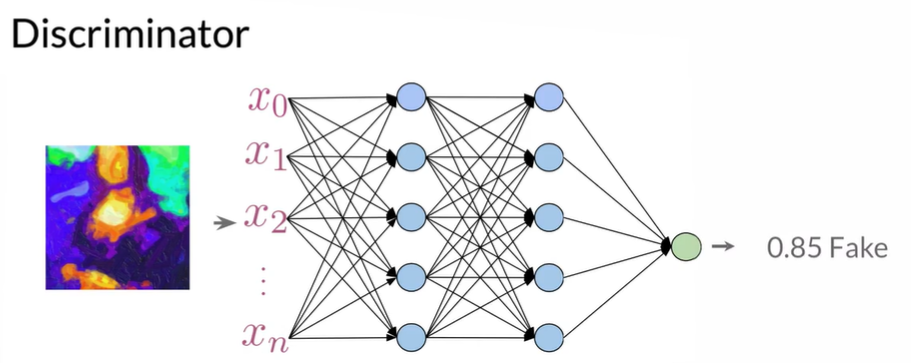
0.85这个概率也会交给Generator
Input features e.g.: RGB pixel values for images
Generator
Use Neural Networks, input: class+noise vector, output: features(image)
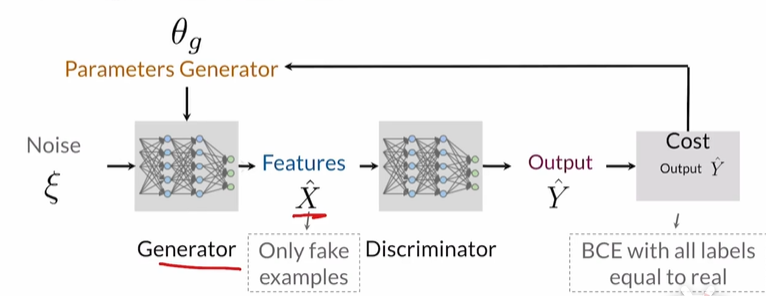
Generator目标是让Fake Example的Y^尽量接近1,而Discriminator目标是让其尽量接近0
当训练的足够好时,Save Generator(θ), use random noise to sample more images.
The generator learns the probability of features X.
BCE Cost Function
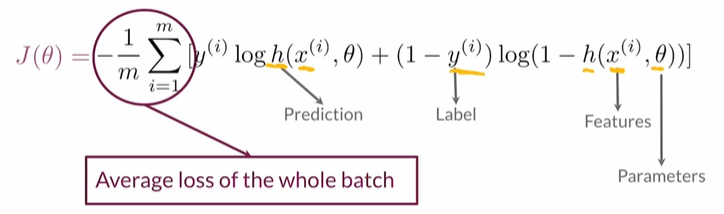
- 前一半:当label y 为0时,为0;当label y 为1时,若Prediction接近1则为0,若Prediction接近0则为负无穷。
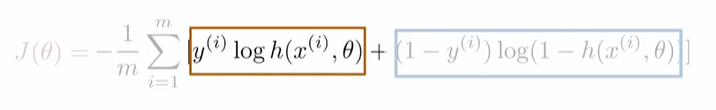
- 后一半:当label y 为1时,为0;当label y 为0时,若Prediction接近0则为1,若Prediction接近1则为负无穷。
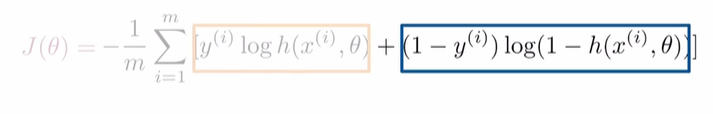
- 综合起来,如果Prediction与label相比非常不准确,则最终的值很大。
Putting it Together
- 最开始,Discriminator和Generator的水平应该相近。
- Discriminator的任务难度比Generator更简单。
- 若Discriminator过于强大,Generator生成的假图片都被判别为100%fake,100%fake对于Generator没有意义,因为其不知道向哪个方向改进。
Coding
- PyTorch vs TensorFlow
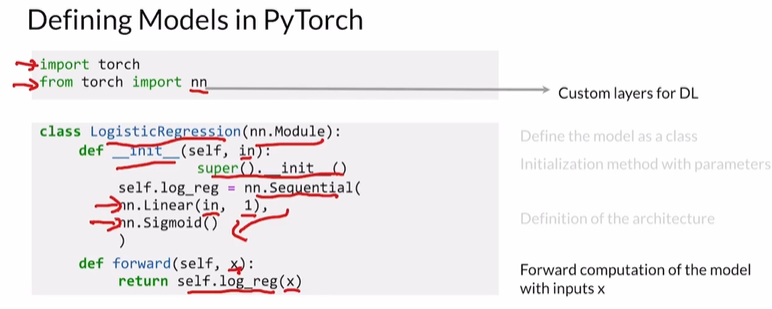
Initialization of the model

Cost function

Optimizer: stochastic gradient descent (随机梯度下降),lr为learning rate

Training loop for number of epochs

1.3 More Components
Activations
Activation functions are non-linear (to approximate complex functions) and differentiable (for back propagation)
ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit)
- Problem: Dying ReLU problem
Leaky ReLU:
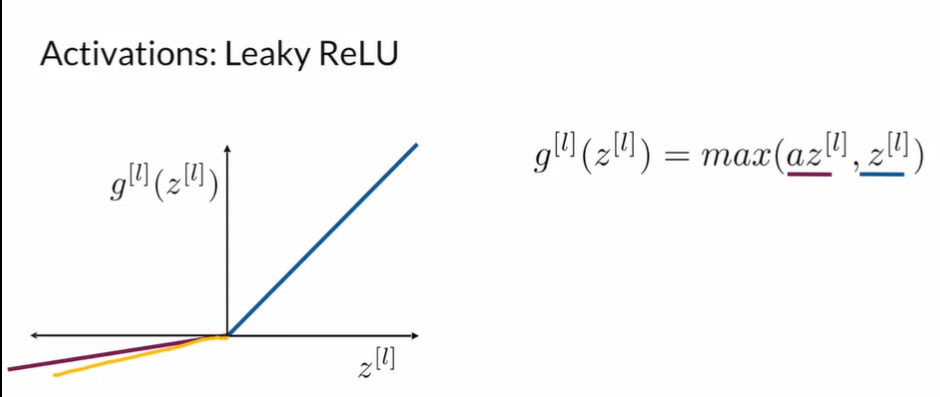
Sigmoid:
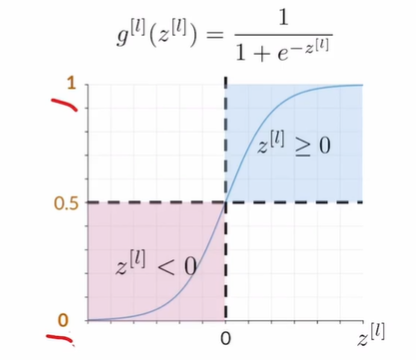
- often used for the last layer
- Problem: vanishing gradient in saturation problems
Tanh (Hyperbolic Tangent):
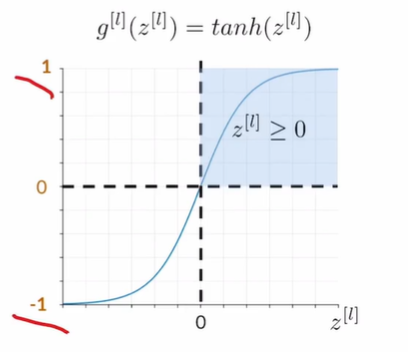
between -1 and 1
Batch Normalization
applied on training data and test data.
- Batch normalization smooths the cost function
- Batch normalization reduces the internal covariance shift
- Batch normalization speeds up learning
Convolution
- scan the image to detect useful features
- Just element-wise products and sums
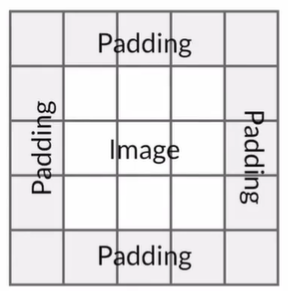
Stride&Padding
Stride: determines how the filter scans the image
Padding: gives similar importance to the edges and the center
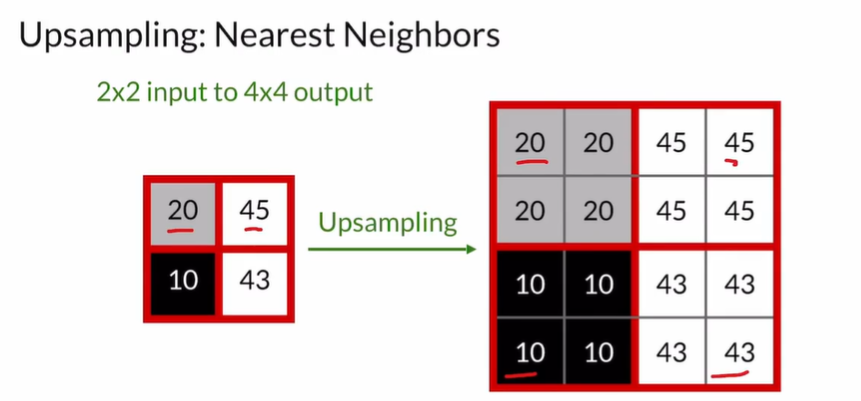
Pooling&Upsampling
Pooling: reduces the size of the input
Upsampling: increases the size of the input
Difference with convolution: Pooling and Upsampling have no learnable parameters, so they involve no learning.
Transposed Convolution
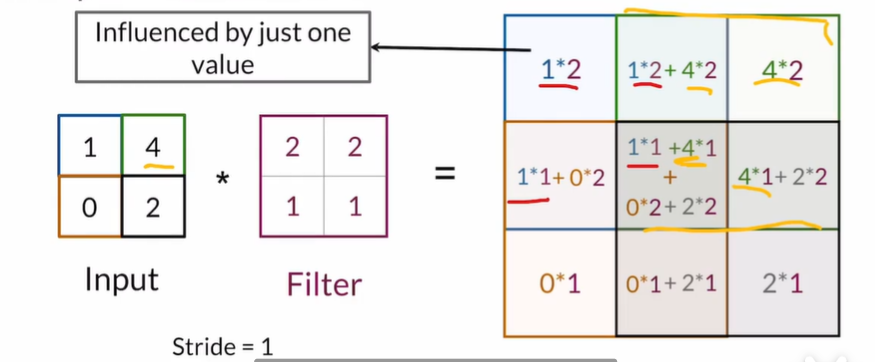
- have learnable parameters
- Problem: results have a checkerboard pattern
1.4 Some Problems of Traditional GANs
Mode Collapse
- Mode Collapse happens when the generator gets stuck in one mode.
Problems with BCE loss
- Flat regions on the cost function = vanishing gradients
